Circles
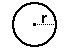
a circle |
Definition: A circle is the
locus of all points equidistant from a central point.
Definitions Related to Circles
arc: a curved line that is part of the circumference of a circle
chord: a line segment within a circle
that touches 2 points on the circle.
circumference: the distance around the circle.
diameter: the longest
distance from one end of a circle to the other.
origin: the center of the circle
pi (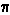 ): A number, 3.141592..., equal to (the circumference) / (the diameter) of any circle. ): A number, 3.141592..., equal to (the circumference) / (the diameter) of any circle.
radius: distance from
center of circle to any point on it.
sector: is like a slice of pie (a circle wedge).
tangent of circle:
a line perpendicular to the radius that touches ONLY one point on the circle. |
diameter
= 2 x radius of circle
Circumference of Circle = PI x diameter = 2 PI x radius
where PI
=

= 3.141592...
Area of Circle:
area = PI r2 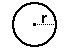
Length of a Circular Arc: (with central angle 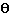 )
)
if the angle  is in degrees, then length =
is in degrees, then length =  x (PI/180) x r
x (PI/180) x r
if the angle  is in radians, then length = r x
is in radians, then length = r x 
Area of Circle Sector: (with central angle  )
)
if the angle  is in degrees, then area = (
is in degrees, then area = ( /360) PI r2
/360) PI r2
if the angle  is in radians, then area = (
is in radians, then area = ( /2) r2
/2) r2
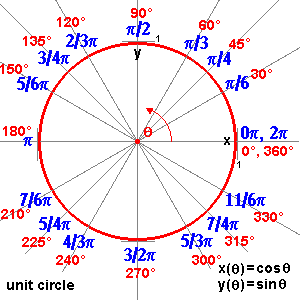
Equation of Circle: (cartesian coordinates)
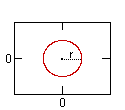
for a circle with center (j, k) and radius (r):
(x-j)2 + (y-k)2
= r2
Equation of Circle: (polar coordinates)
for a circle with center (0,
0): r( ) = radius
) = radius
for a circle with center with polar coordinates: (c, 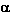 ) and radius a:
) and radius a:
r2 - 2cr cos( -
-  ) + c2 = a2
) + c2 = a2
Equation of a Circle: (parametric coordinates)
for a circle with origin
(j, k) and radius r:
x(t) = r cos(t) + j y(t) = r sin(t) + k